Simulated multiple reference training improves low-resource machine translation
Huda Khayrallah, Brian Thompson, Matt Post, Philipp Koehn
Machine Translation and Multilinguality Short Paper

You can open the pre-recorded video in a separate window.
Abstract:
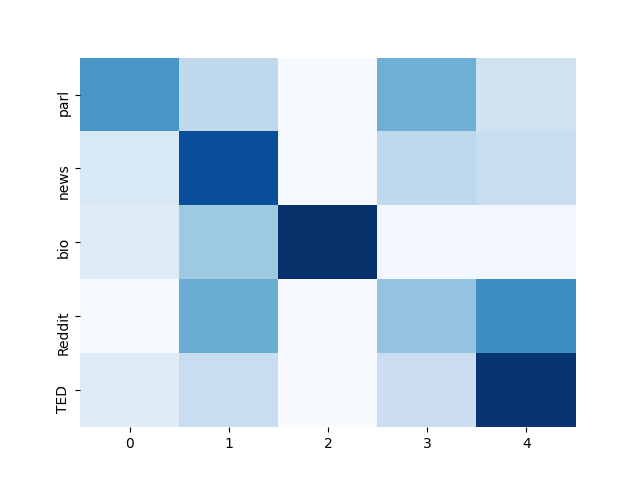
Many valid translations exist for a given sentence, yet machine translation (MT) is trained with a single reference translation, exacerbating data sparsity in low-resource settings. We introduce Simulated Multiple Reference Training (SMRT), a novel MT training method that approximates the full space of possible translations by sampling a paraphrase of the reference sentence from a paraphraser and training the MT model to predict the paraphraser’s distribution over possible tokens. We demonstrate the effectiveness of SMRT in low-resource settings when translating to English, with improvements of 1.2 to 7.0 BLEU. We also find SMRT is complementary to back-translation.
NOTE: Video may display a random order of authors.
Correct author list is at the top of this page.
Connected Papers in EMNLP2020
Similar Papers
Distilling Multiple Domains for Neural Machine Translation
Anna Currey, Prashant Mathur, Georgiana Dinu,
Uncertainty-Aware Semantic Augmentation for Neural Machine Translation
Xiangpeng Wei, Heng Yu, Yue Hu, Rongxiang Weng, Luxi Xing, Weihua Luo,

Language Model Prior for Low-Resource Neural Machine Translation
Christos Baziotis, Barry Haddow, Alexandra Birch,
Dynamic Data Selection and Weighting for Iterative Back-Translation
Zi-Yi Dou, Antonios Anastasopoulos, Graham Neubig,
