Pareto Probing: Trading Off Accuracy for Complexity
Tiago Pimentel, Naomi Saphra, Adina Williams, Ryan Cotterell
Interpretability and Analysis of Models for NLP Long Paper

You can open the pre-recorded video in a separate window.
Abstract:
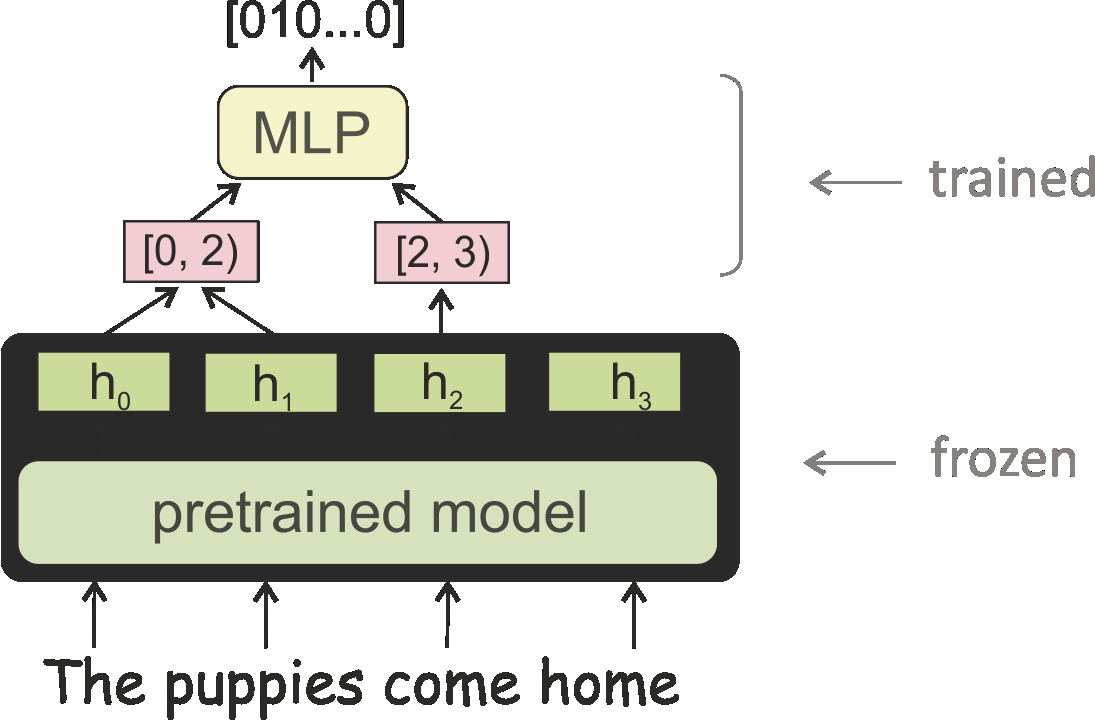
The question of how to probe contextual word representations in a way that is principled and useful has seen significant recent attention. In our contribution to this discussion, we argue, first, for a probe metric that reflects the trade-off between probe complexity and performance: the Pareto hypervolume. To measure complexity, we present a number of parametric and non-parametric metrics. Our experiments with such metrics show that probe's performance curves often fail to align with widely accepted rankings between language representations (with, e.g., non-contextual representations outperforming contextual ones). These results lead us to argue, second, that common simplistic probe tasks such as POS labeling and dependency arc labeling, are inadequate to evaluate the properties encoded in contextual word representations. We propose full dependency parsing as an example probe task, and demonstrate it with the Pareto hypervolume. In support of our arguments, the results of this illustrative experiment conform closer to accepted rankings among contextual word representations.
NOTE: Video may display a random order of authors.
Correct author list is at the top of this page.
Connected Papers in EMNLP2020
Similar Papers
A matter of framing: The impact of linguistic formalism on probing results
Ilia Kuznetsov, Iryna Gurevych,

Methods for Numeracy-Preserving Word Embeddings
Dhanasekar Sundararaman, Shijing Si, Vivek Subramanian, Guoyin Wang, Devamanyu Hazarika, Lawrence Carin,
Compositional and Lexical Semantics in RoBERTa, BERT and DistilBERT: A Case Study on CoQA
Ieva Staliūnaitė, Ignacio Iacobacci,