Toward Micro-Dialect Identification in Diaglossic and Code-Switched Environments
Muhammad Abdul-Mageed, Chiyu Zhang, AbdelRahim Elmadany, Lyle Ungar
Computational Social Science and Social Media Long Paper

You can open the pre-recorded video in a separate window.
Abstract:
Although prediction of dialects is an important language processing task, with a wide range of applications, existing work is largely limited to coarse-grained varieties. Inspired by geolocation research, we propose the novel task of Micro-Dialect Identification (MDI) and introduce MARBERT, a new language model with striking abilities to predict a fine-grained variety (as small as that of a city) given a single, short message. For modeling, we offer a range of novel spatially and linguistically-motivated multi-task learning models. To showcase the utility of our models, we introduce a new, large-scale dataset of Arabic micro-varieties (low-resource) suited to our tasks. MARBERT predicts micro-dialects with 9.9% F1, 76 better than a majority class baseline. Our new language model also establishes new state-ofthe- art on several external tasks.
NOTE: Video may display a random order of authors.
Correct author list is at the top of this page.
Connected Papers in EMNLP2020
Similar Papers
Tackling the Low-resource Challenge for Canonical Segmentation
Manuel Mager, Özlem Çetinoğlu, Katharina Kann,

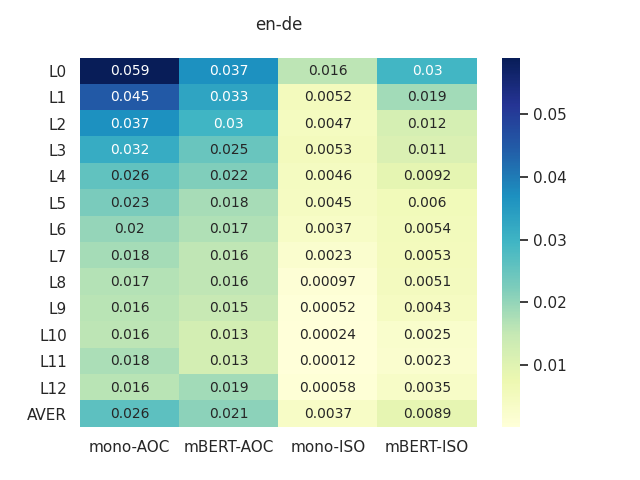
When Hearst Is not Enough: Improving Hypernymy Detection from Corpus with Distributional Models
Changlong Yu, Jialong Han, Peifeng Wang, Yangqiu Song, Hongming Zhang, Wilfred Ng, Shuming Shi,
XL-WiC: A Multilingual Benchmark for Evaluating Semantic Contextualization
Alessandro Raganato, Tommaso Pasini, Jose Camacho-Collados, Mohammad Taher Pilehvar,
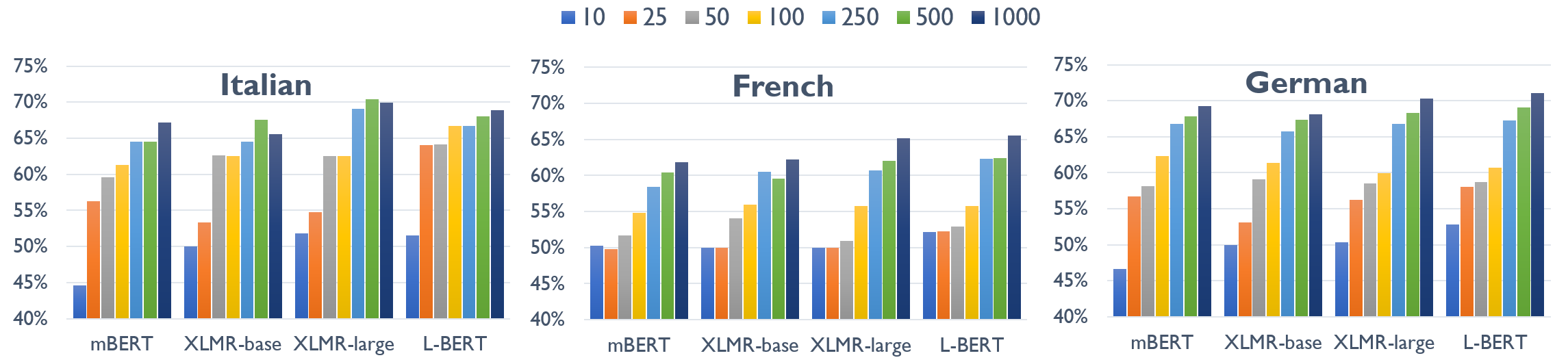
Probing Pretrained Language Models for Lexical Semantics
Ivan Vulić, Edoardo Maria Ponti, Robert Litschko, Goran Glavaš, Anna Korhonen,