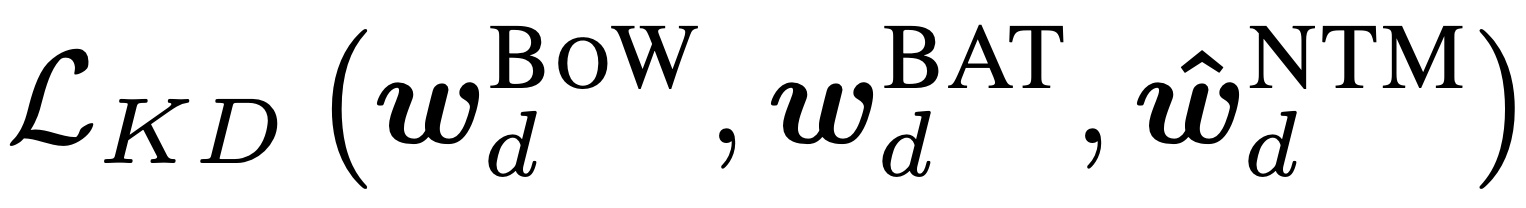Incorporating Behavioral Hypotheses for Query Generation
Ruey-Cheng Chen, Chia-Jung Lee
Information Retrieval and Text Mining Short Paper

You can open the pre-recorded video in a separate window.
Abstract:
Generative neural networks have been shown effective on query suggestion. Commonly posed as a conditional generation problem, the task aims to leverage earlier inputs from users in a search session to predict queries that they will likely issue at a later time. User inputs come in various forms such as querying and clicking, each of which can imply different semantic signals channeled through the corresponding behavioral patterns. This paper induces these behavioral biases as hypotheses for query generation, where a generic encoder-decoder Transformer framework is presented to aggregate arbitrary hypotheses of choice. Our experimental results show that the proposed approach leads to significant improvements on top-k word error rate and Bert F1 Score compared to a recent BART model.
NOTE: Video may display a random order of authors.
Correct author list is at the top of this page.
Connected Papers in EMNLP2020
Similar Papers
PathQG: Neural Question Generation from Facts
Siyuan Wang, Zhongyu Wei, Zhihao Fan, Zengfeng Huang, Weijian Sun, Qi Zhang, Xuanjing Huang,

Improving Neural Topic Models using Knowledge Distillation
Alexander Miserlis Hoyle, Pranav Goel, Philip Resnik,