Sketch-Driven Regular Expression Generation from Natural Language and Examples
Xi Ye, Qiaochu Chen, Xinyu Wang, Isil Dillig, Greg Durrett
Semantics: Sentence-level Semantics, Textual Inference and Other areas Tacl Paper

You can open the pre-recorded video in a separate window.
Abstract:
Recent systems for converting natural language descriptions into regular expressions (regexes) have achieved some success, but typically deal with short, formulaic text and can only produce simple regexes. Realworld regexes are complex, hard to describe with brief sentences, and sometimes require examples to fully convey the user’s intent. We present a framework for regex synthesis in this setting where both natural language (NL) and examples are available. First, a semantic parser (either grammar-based or neural) maps the natural language description into an intermediate sketch, which is an incomplete regex containing holes to denote missing components. Then a program synthesizer searches over the regex space defined by the sketch and finds a regex that is consistent with the given string examples. Our semantic parser can be trained purely from weak supervision based on correctness of the synthesized regex, or it can leverage heuristically-derived sketches. We evaluate on two prior datasets (Kushman and Barzilay, 2013; Locascio et al., 2016) and a real-world dataset from Stack Overflow. Our system achieves state-of-the-art performance on the prior datasets and solves 57% of the real-world dataset, which existing neural systems completely fail on.
NOTE: Video may display a random order of authors.
Correct author list is at the top of this page.
Connected Papers in EMNLP2020
Similar Papers
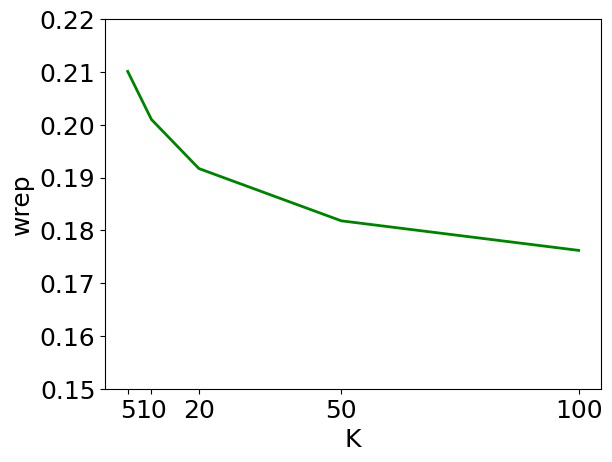
Grounded Compositional Outputs for Adaptive Language Modeling
Nikolaos Pappas, Phoebe Mulcaire, Noah A. Smith,
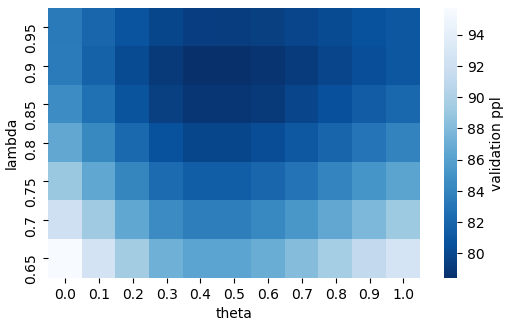
MEGATRON-CNTRL: Controllable Story Generation with External Knowledge Using Large-Scale Language Models
Peng Xu, Mostofa Patwary, Mohammad Shoeybi, Raul Puri, Pascale Fung, Anima Anandkumar, Bryan Catanzaro,
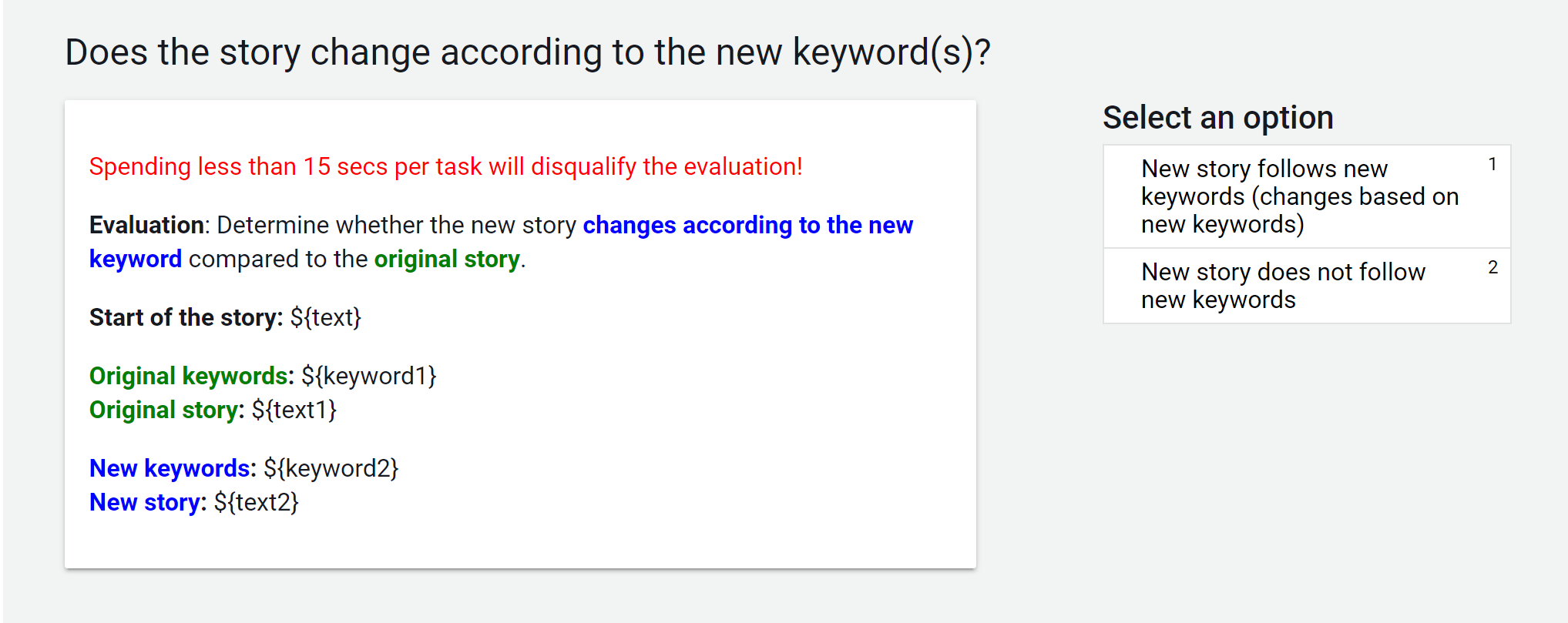
Universal Natural Language Processing with Limited Annotations: Try Few-shot Textual Entailment as a Start
Wenpeng Yin, Nazneen Fatema Rajani, Dragomir Radev, Richard Socher, Caiming Xiong,