Vokenization: Improving Language Understanding with Contextualized, Visual-Grounded Supervision
Hao Tan, Mohit Bansal
Language Grounding to Vision, Robotics and Beyond Long Paper

You can open the pre-recorded video in a separate window.
Abstract:
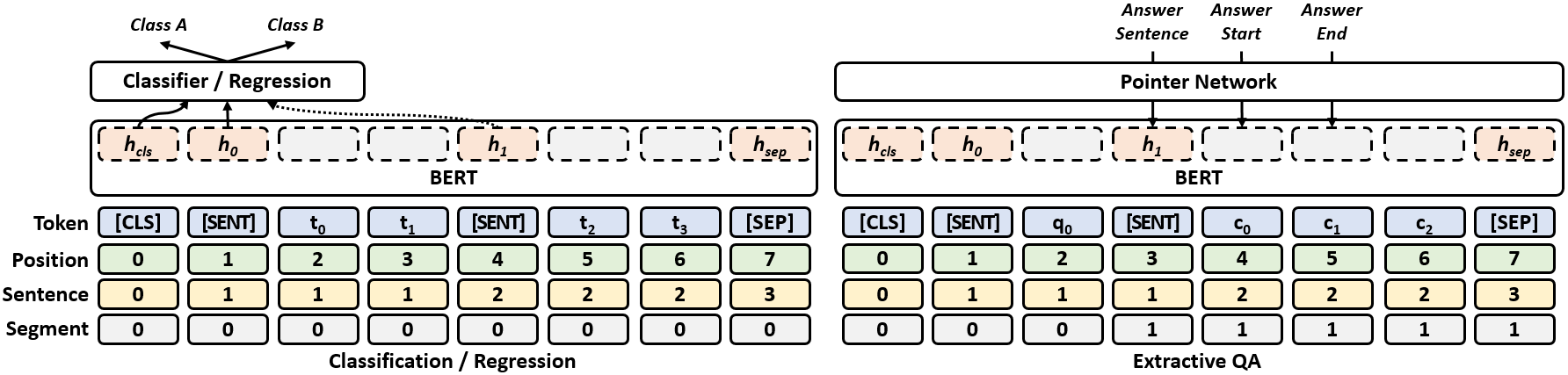
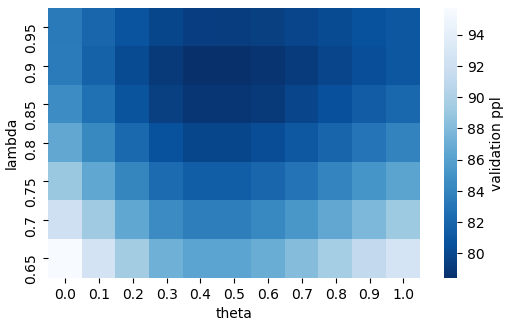
Humans learn language by listening, speaking, writing, reading, and also, via interaction with the multimodal real world. Existing language pre-training frameworks show the effectiveness of text-only self-supervision while we explore the idea of a visually-supervised language model in this paper. We find that the main reason hindering this exploration is the large divergence in magnitude and distributions between the visually-grounded language datasets and pure-language corpora. Therefore, we develop a technique named “vokenization” that extrapolates multimodal alignments to language-only data by contextually mapping language tokens to their related images (which we call “vokens”). The “vokenizer” is trained on relatively small image captioning datasets and we then apply it to generate vokens for large language corpora. Trained with these contextually generated vokens, our visually-supervised language models show consistent improvements over self-supervised alternatives on multiple pure-language tasks such as GLUE, SQuAD, and SWAG.
NOTE: Video may display a random order of authors.
Correct author list is at the top of this page.
Connected Papers in EMNLP2020
Similar Papers
SLM: Learning a Discourse Language Representation with Sentence Unshuffling
Haejun Lee, Drew A. Hudson, Kangwook Lee, Christopher D. Manning,
Grounded Compositional Outputs for Adaptive Language Modeling
Nikolaos Pappas, Phoebe Mulcaire, Noah A. Smith,
Visually Grounded Continual Learning of Compositional Phrases
Xisen Jin, Junyi Du, Arka Sadhu, Ram Nevatia, Xiang Ren,

MAF: Multimodal Alignment Framework for Weakly-Supervised Phrase Grounding
Qinxin Wang, Hao Tan, Sheng Shen, Michael Mahoney, Zhewei Yao,
