Digital Voicing of Silent Speech
David Gaddy, Dan Klein
Speech and Multimodality Long Paper

You can open the pre-recorded video in a separate window.
Abstract:
In this paper, we consider the task of digitally voicing silent speech, where silently mouthed words are converted to audible speech based on electromyography (EMG) sensor measurements that capture muscle impulses. While prior work has focused on training speech synthesis models from EMG collected during vocalized speech, we are the first to train from EMG collected during silently articulated speech. We introduce a method of training on silent EMG by transferring audio targets from vocalized to silent signals. Our method greatly improves intelligibility of audio generated from silent EMG compared to a baseline that only trains with vocalized data, decreasing transcription word error rate from 64% to 4% in one data condition and 88% to 68% in another. To spur further development on this task, we share our new dataset of silent and vocalized facial EMG measurements.
NOTE: Video may display a random order of authors.
Correct author list is at the top of this page.
Connected Papers in EMNLP2020
Similar Papers
The role of context in neural pitch accent detection in English
Elizabeth Nielsen, Mark Steedman, Sharon Goldwater,
Consistent Transcription and Translation of Speech
Matthias Sperber, Hendra Setiawan, Christian Gollan, Udhay Nallasamy, Matthias Paulik,

Pre-Training Transformers as Energy-Based Cloze Models
Kevin Clark, Minh-Thang Luong, Quoc Le, Christopher D. Manning,
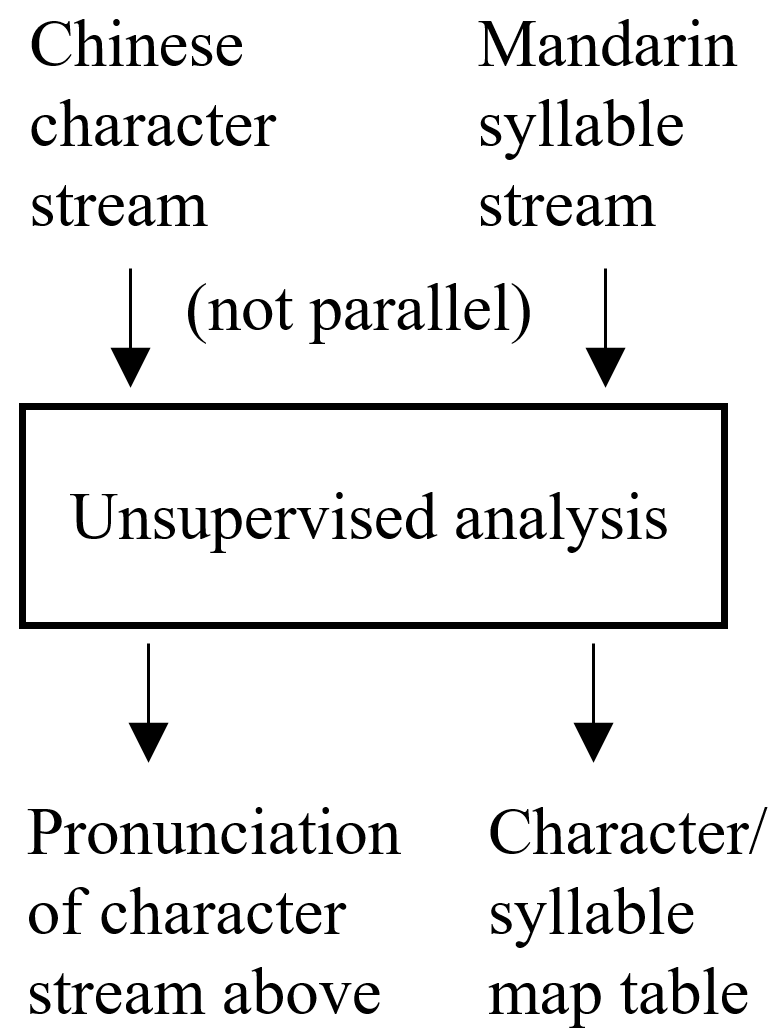
Learning to Pronounce Chinese Without a Pronunciation Dictionary
Christopher Chu, Scot Fang, Kevin Knight,